Throughout our lives, intricate mechanisms regulate our body’s growth. The length of our arms and legs, the size of our heads, and the alignment of our teeth and jaws all tend to match up. This seems to happen automatically, so few of us pause to wonder why. Yet for some people, a subtle glitch in the growth-hormone (GH) secretion system can lead to a dramatic and visual derailment of this natural process. With it, multiple serious health problems arise.
Acromegaly and gigantism
Divergences from what we consider ‘standard growth’ can occur either during developmental growth in children (gigantism) or continued/re-started growth in later life (acromegaly), with both being caused by an overproduction of growth hormone. GH excess before a child’s growth plates are closed leads to increased height – thus the term ‘gigantism’ – as well as abnormal growth of hands, feet, and facial features. Acromegaly – GH excess after the bone growth plates have closed – leads to the enlargement of hands, feet, facial features, and other parts of the body but without an increase in height. In addition to these obvious outward manifestations, various other comorbidities and complications occur in patients with excessive GH secretion, including respiratory, cardiovascular, metabolic, endocrine, gastrointestinal, and skeletal system complications.
In 95% of clinical cases, the root of acromegaly and giantism lies in a pituitary adenoma. This noncancerous (benign) tumor develops in the pea-sized pituitary gland, located at the base of the brain. Gigantism and acromegaly cannot be prevented. However, early detection and treatment may prevent the disease from getting worse and help avoid complications.
The search for active pharmaceutical ingredients
When the pituitary adenoma is small and well-defined, surgical resection constitutes the first line of treatment, leading to cure in about 80% of gigantism patients and 50% of acromegaly patients.
However, surgical solutions are often either impossible or only partially effective for larger or dispersed pituitary adenomas, which means a large portion of patients rely on non-surgical interventions and therapies.
GH-lowering therapies utilizing synthetic analogs of somatostatin emerged as an effective treatment for these patients. Somatostatin is an endogenous peptide hormone that regulates the endocrine system via interaction with G protein-coupled somatostatin receptors, inhibiting the release of numerous secondary hormones in the pituitary gland, including growth hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone. As for many endogenous peptides, the half-life of these molecules is mere minutes, reducing the therapeutic window for effective treatment.
At a glance: Acromegaly therapy
Prevalence: Between 7-13 cases per 100,000
Incidence: About 1.1 cases per 100,000
Median Age of Diagnosis: 40-50 years, usually noticed between 4-10 years after onset
Cause: 95% of cases due to pituitary adenoma
Treatment: Transsphenoidal adenomectomy or life-long somatostatin receptor ligands (SRL)
Challenges: Surgical cure not achievable in ~50% of patients, SRL therapy can elicit resistance, fail biochemical control, struggle with patient compliance to treatment and pose an economic burden
Opportunities: New oral octreotide formulations
Octreotide – A transformative peptide molecule
Octreotide acetate, a synthetically produced longer-acting therapeutic octapeptide analog of somatostatin, has been monumental in reducing the levels of GH and insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1) in patients.
The World Health Organization lists octreotide as an essential medicine for its potential to alleviate the many challenges of acromegaly faced by patients worldwide. Octreotide also finds use a as therapeutic in other disease areas, such as neuroendocrine tumors (NETs), secretory diarrhea and other endocrine disorders. With a global market of around USD 1.4 billion and US patent protections ending in 2014, multiple drug manufacturers have been working on developing generic octreotide formulations for patients to increase accessibility globally.
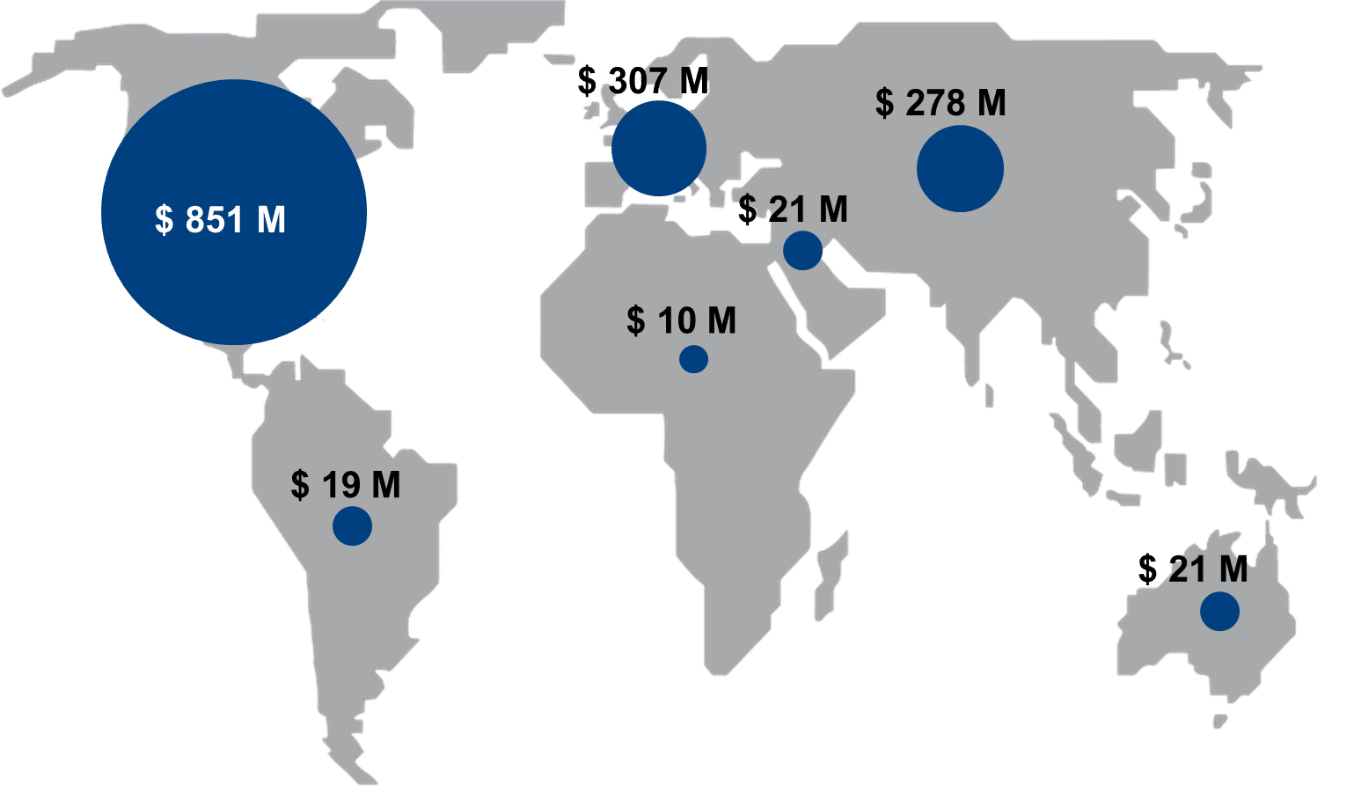
Sales of octreotide per region in 2022, Data Source: IQVIA
Disease control and quality of life with synthetic somatostatin analogs
Like many treatments, current octreotide acetate therapies are not without challenges. In acromegaly, developing drug resistance and ineffective biochemical or symptom control in a subset of patients still pose limitations today. Compliance to injection regimens can also be a barrier. Since 1998, the previously required daily injections have been mostly replaced by long-acting release (LAR) therapy forms administered only once a month.
Over the years, the clinical approach to treating acromegaly has also evolved. While surgery targeting the pituitary remains the primary choice for many cases, the emergence of advanced pharmacological treatments promises enhanced disease management. Notable developments in the pipeline include:
- Injectable octreotide bound in a liquid crystal mix
- An advanced SR-multiligand known for its keen ability to suppress GH
- Cutting-edge antisense oligonucleotide aiming at the GH receptor
- Fresh formulations of Somatostatin Receptor Ligands such as oral octreotide capsules
Interestingly, a comparative Phase III trial explored the oral intake of octreotide in patients who were already responding well to the long-acting release (LAR) form of octreotide. The results demonstrated that shifting to an oral form maintained effective biochemical control. Even more promising was the observation that patients preferred the oral route, resulting in better treatment regimen adherence. However, one point of consideration for oral intake is the need for fasting to optimize octreotide levels in the bloodstream. In the Phase III trial, a notable majority (over 90%) complied with the dietary restrictions.
While new oral formulations promise equal or better disease control and quality of life for patients, they require 30-60 times higher octreotide acetate concentrations. This places heavy demand on complex API manufacturers to scale up production to meet patient and affordability demands.
Peek behind the curtain of Octreotide
We recently published a case study that chronicled the cost-effective 15x upscaling of octreotide acetate. It transparently highlights the challenges and exciting improvements in terms of quality, prize, and patient impact such a large-scale process can offer.
The road for acromegaly patients has been challenging. But with ever-improving pharmaceutical treatments and more affordable access, the symptoms, mortality risk and quality of life can normalize and empower most patients to lead a full life.
Ultimately, this is the impact that gives our work meaning every day.
References:
Acromegaly | Nature Reviews Disease Primers
New therapeutic agents for acromegaly – PubMed (nih.gov)
A consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of acromegaly complications – PubMed (nih.gov)
Subscribe to our general newsletter
"*" indicates required fields
